
Pic Credit: Unsplash
Intending to make India a global manufacturing hub, the Government of India (GoI) gave an open call to manufacturers from across the world to start manufacturing in India. International companies were focused on their competitive strengths such as cost leadership, technology, innovation, lean manufacturing, and defect-free products. Indian manufacturing organizations were challenged to improve their performance to ensure their survival and growth in the fiercely competitive global market. To bring about such improvements Indian manufacturing companies increased their focus on the production of zero defect quality goods, in a cost-effective environment-friendly manner, to create an advantage for them in the marketplace.
With a zero effect zero defect (ZED) maturity model campaign, the GoI was essentially emphasizing quality (by using clean technology) over quantity, thus enabling “Brand India” to get visibility in the manufacturing center stage of the world. It was intended to change from a total dependency on assessment of the final product to identify and correct defects, to an upbeat practice of improving processes such as quality planning, process, and product designing, logistics optimization, efficient resource management, and efficient outsourcing activities. Along with the focus on the quality of products, there was equal stress on the elimination of impact on the environment throughout the supply chain by adequate planning during the process and product design, pre-production, production and maintenance activities, and post-production activities such as disposal or product recycle after use. Overall, the key idea was sustainable development across the supply chain.
ZED Scope
The Model was applicable for all sectors of manufacturing industries with a focus on MSMEs and small businesses. It addressed the quality and ecological needs of customers, society, employees, partners, regulators, and investors.
The benefits from ZED initiatives were:
- Plausible recognition of the Indian manufacturing industry by international customers looking for investment in India
- Efficient operations at lower costs
- Superior quality and higher revenues
- Better social and environmental benefits
- Employment generation
ZED Ecosystem
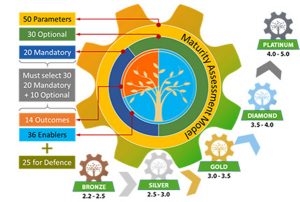
The ecosystem of ZED was comprised of dynamic systems and processes working in synergy with specified roles. The sector-specific models were aligned with 50 Parameters across 10 disciplines:
- Quality Management
- Production Management
- Environmental Management
- Energy Management
- Safety Management
- Natural Resource Management
- Intellectual Property Management
- Human Resource Management
- Design Management
- Performance Management
ZED Maturity Assessment Model
- Any manufacturing MSME may apply for the subsidy
- Focused on encouraging implementation and improvement
- The assessment was carried out to evaluate the maturity of implementation.
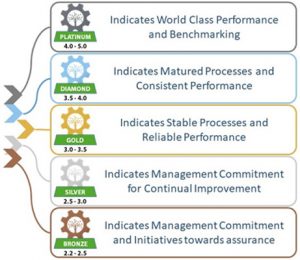
- Result graded in 5 levels:
- Learner (0)
- Beginner (2)
- Organized (3)
- Achiever (4)
- World Class (5)
- MSMEs were eligible for financial subsidy only if the assessment rating was Bronze or above.
Reference
Strategy, & Solutions, B. (n.d.). SBS – Zero defect zero effect. SBS | Strategy and Business Solutions | A Knowledge Organisation & training solutions. https://www.sbsact.com/zed.php#zed-assessment-parameters
