
As the world advances in sophisticated computer systems and the fourth industrial revolution, internet security becomes a major problem for large businesses. These businesses have a complex network of connected machines that they use for their daily and important activities. The end user, who may be an employee of the business, may be the sole target of the criminal, to access sensitive business data, which could lead to significant losses. Traditional methods of tracking theft do not always provide the right information, and delays can result in significant business losses.
In the past few years, there has been a significant rise in the number of world-wide cyber-attacks affecting the network of several large and small businesses in all sectors. Neither the government nor the private sector has been secure from these attacks. The cost to economies is high and the cost to the individual can be catastrophic. According to the Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ), UK, report, every hour, around 1000 cyber-attacks are carried out across the globe. It is seen that in the U.S., the number of cyber intrusions has increased more than seventeen times in the last 5 years. This is a significant rise compared to the other western countries.
Efforts have been made for providing a robust system for protecting against cyber-attacks. However, to our knowledge, none of them make use of the advanced technologies of machine learning and artificial intelligence which we do.
Our method comprises the steps of
- Identify the data from the user’s device that could be used for detecting possible cyberattack.
- Extract features from the data using advanced neural network techniques.
- Classify the data and Determine potential cyberattack or risk of it.
- Perform the required action to secure the user’s device or alert/ notify the user.
The block diagram of the system is as follows:
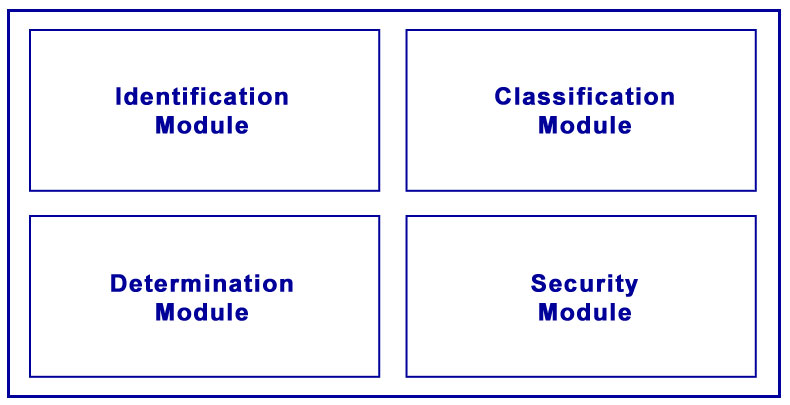
The identification module identifies the data from the user’s device to be analysed for a cyberattack, the classification module classifies and extracts features using a supervised multi-class classifier created by a plurality of layers of artificial neural network, a determination module determines a potential cyberattack based on a predefined threshold and a security module provides an alert or the required security for protecting a user device from the potential cyberattack using supervised data mining method comprising a decision tree, an ensemble method, a regression analysis and a vector method.
Artificial neural network generally refers to the model of connected data that can be weighted based on the input data and can be used to estimate a function. A deep belief neural network can also use the unsupervised training of the input data to detect any number of features within the data. Feature extraction refers to the process for deriving vectors or values that can be analysed as part of machine learning. The classification module can classify the data in several ways–the artificial neural networks can perform hierarchical feature extraction, semi-supervised machine learning and unsupervised machine learning.
In the determination module, the predefined threshold can include a degree of likelihood that the classification of data accurately identifies the possible cyberattack. It can also identify the percentage of cyberattacks that have occurred over a given period. The classification of the data can pass that predefined threshold if the percentage is high enough. Also, multiple classifiers can also be used for a different classification of the data.
The predefined threshold can be used to determine the best classification that can be used to detect the cyberattack on the user’s device. The security module can minimize potential Internet attacks on a user’s device or alert the user about potential Internet attacks. The security model converts features extracted from training data into leaf nodes using a word bag model. This model usually refers to data representation, especially text, which can track the presence or frequency of different data (e.g., words) within each document and may be rated as important to change features. The decision tree usually refers to predictable models with a branch structure that reflects the results of the observation. Vector machine usually refers to learning models that use algorithms to detect programming patterns.
In conclusion, we have used the advanced technologies of machine learning and artificial intelligence to provide cybersecurity which is a big concern in this era of complex computer programs and the fourth industrial revolution.
Dr. Shobana Padmanabhan and Dr. Chetan Shelke
Alliance College of Engineering and Design
